Flexible Medical Bioelectronics

Mechanical mismatch between biological tissue and digital interface is a long-standing challenge for wearable and implantable bioelectronic devices. With the revolutionary advances in flexible materials and electronics, medical bioelectronics can adapt to varying body sites, from skin, muscle, eyes, brain to heart and other deep organs. Such flexible electronic interfaces enable intimate interaction between biological and digital world, supporting unprecedented diagnostic and theraputic approaches and significantly improving the biocompatibility of medical bioelectronics.
Wireless Bioelectronic Technologies

Smart integration of advanced wireless techniques and stimulus-driven materials heralds the advent of new implantable and wearable bioelectronics. It may identify varying diseases at early stage by patients at home, showing particular value during pandemics like COVID-19. More importantly, extra data can reshape our understanding of brain activities, cancer progression as well as other diseases. It will also allow treatment outside centralized healthcare settings, and make prompt intervention possible, leading to better patient outcomes.
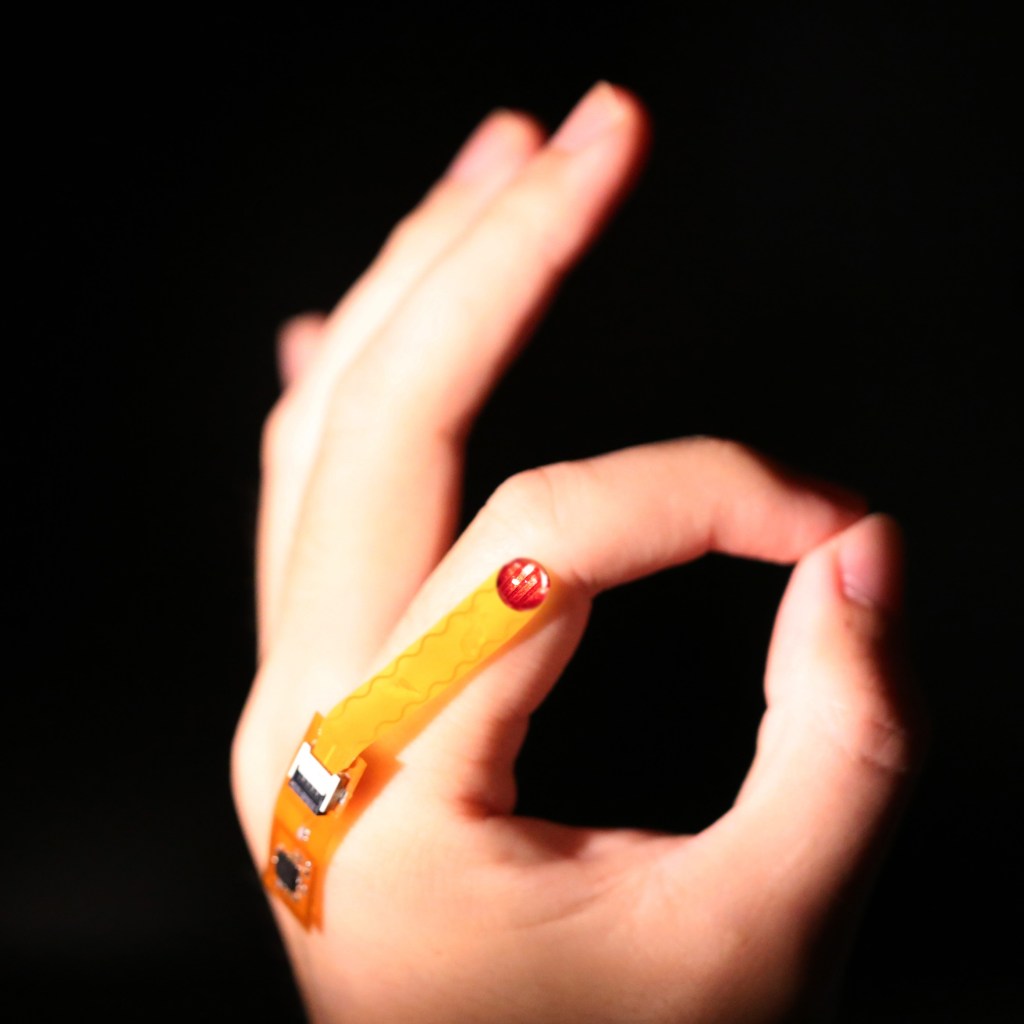
Stimulus-Responsive Materials
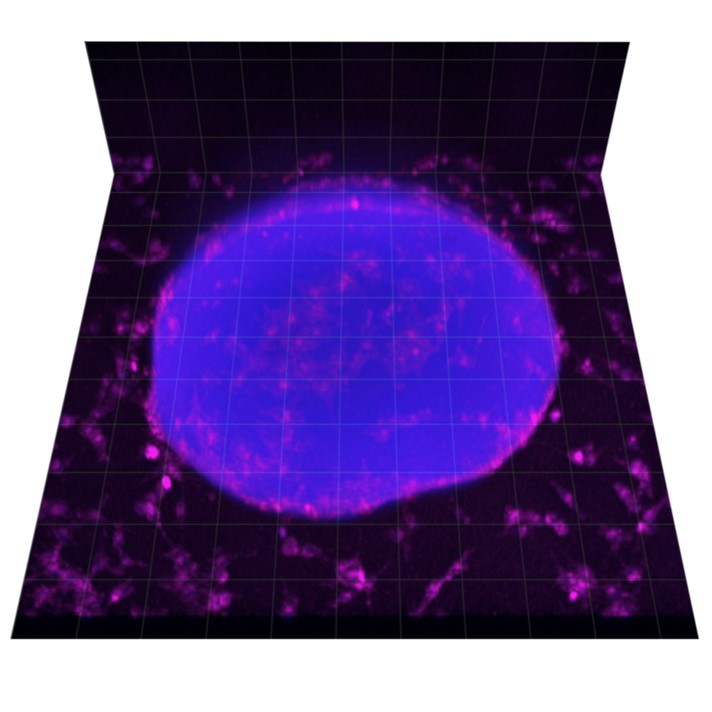
Stimulus-responsive materials represent a class of materials that detect physical or biochemical stimuli and intelligently elicit mechanical, electrical, or other responses. For instance, the bio-responsive hydrogels can transduce and enhance biomolecular signal, in place of power-consuming electronic amplifiers. These smart materials made unobtrusive bioelectronic sensors possible, enabling people to monitor epidermal and deep wound complications that existing technologies could not achieve.
Biomedical Micro/Nano-Robotics
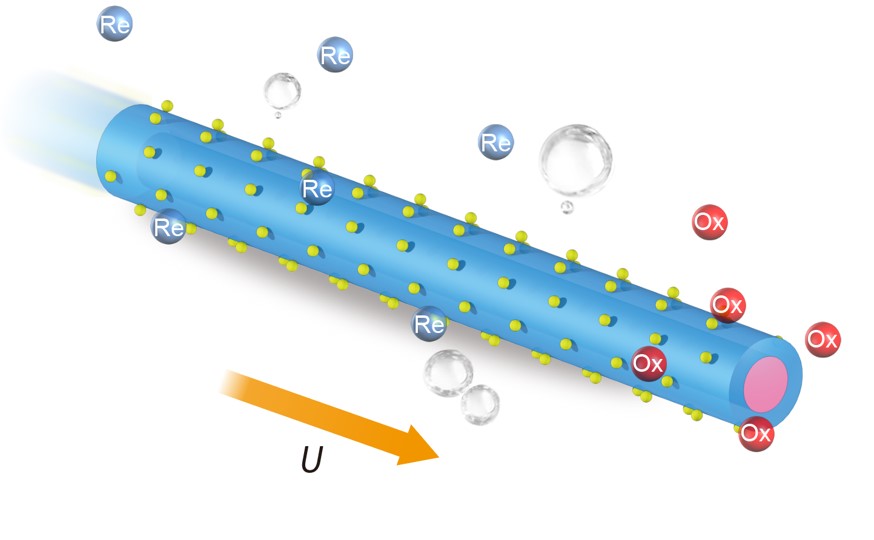
Over the last decades, scientists have endeavored to develop nanomachines and envisioned that these tiny machines could bring in revolutionary biomedical applications. Micro/nanorobots can harvest energy from the surrounding environment and target hard-to-reach diseases. Such well-designed micro/nanorobots may open up new opportunities for the realization of swarming intelligence as well as non-invasive diagnosis and targeted therapy.